DR. BRIJESH PRAJAPAT
MBBS, MD, DM
(PULMONARY & CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE)
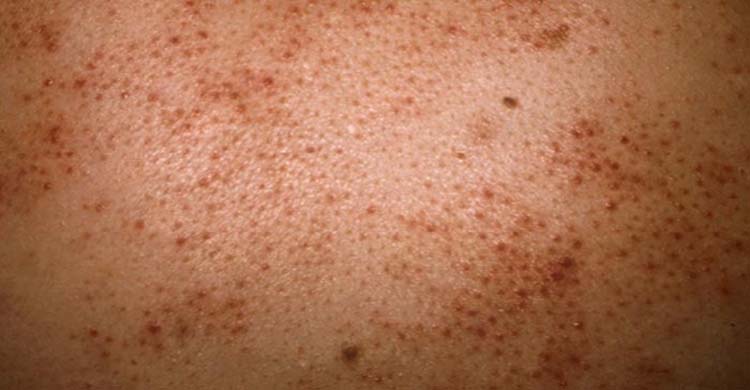
Eosinophilia is a condition that is associated with high levels of eosinophils in the blood or bodily tissues. Eosinophils are a specific type of white blood cells that play an important role in fighting diseases and warding off infections in the body. Your body has the ability to handle eosinophil levels between a certain range in the blood. However, when the total eosinophil count exceeds the normal range, it can cause inflammation. People with eosinophilia can experience symptoms like skin rashes, wheezing, and coughs and even abdominal pain and diarrhea in some cases.
White blood cells in your body are vital to your body’s immune system. White blood cells are often released by the body to fight off infections. The human body does not usually produce an excess amount of eosinophils in blood. Therefore, when then the body releases more than the usual amount, it is usually indicative of an infection that may be present.
Eosinophilia can affect both adults and children. The next few chapters feature the discussion of eosinophilia causes, symptoms, treatments and diagnosis in further detail.
1. What causes eosinophils count to be high?
There are many reasons for an increased eosinophil count in the body. Some major eosinophilia causes include parasitic infections, asthma allergic disorders such as season allergies, food allergies, eczema and other skin disorders, and certain types of cancers.
2. What are some of the causes of low eosinophils in the blood?
A low eosinophil count in the blood may signify alcohol intoxication or a link to Cushing’s syndrome that is commonly associated with the overproduction of a hormone known as cortisol which contributes to the lower than normal level of eosinophils in the blood.
3. What is the absolute eosinophil count normal value?
A normal absolute eosinophil count refers to the number of eosinophils that is normally present in a person who is healthy. An AEC count value that lies in between 40-400 eosinophil cells per ml of blood is considered normal.
4. How is eosinophilia treated? What are some of the eosinophilia medicines that are administered to affected patients?
Eosinophilia treatments differ from person to person depending on the symptoms, location of eosinophilia, underlying cause and the intensity of the condition. Mild cases are usually observed and monitored. Other treatments include discontinuation of certain medications causing allergic reactions, increasing treatment for asthma and atopical disorders, and administering anti-parasitic medication if the reason for eosinophilia in a patient was due to a parasitic infection. In cases of hypereosinophilia, corticosteroids are usually administered to bring down the level of eosinophils in the blood.
5. Are there any home remedies for eosinophilia?
There aren’t any home remedies for eosinophilia per se, at least ones that would cure eosinophilia. Eosinophilia home treatments may assist in managing symptoms however, it is important to consult a physician before implementing any eosinophilia home treatments of your own.