DR. BRIJESH PRAJAPAT
MBBS, MD, DM
(PULMONARY & CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE)
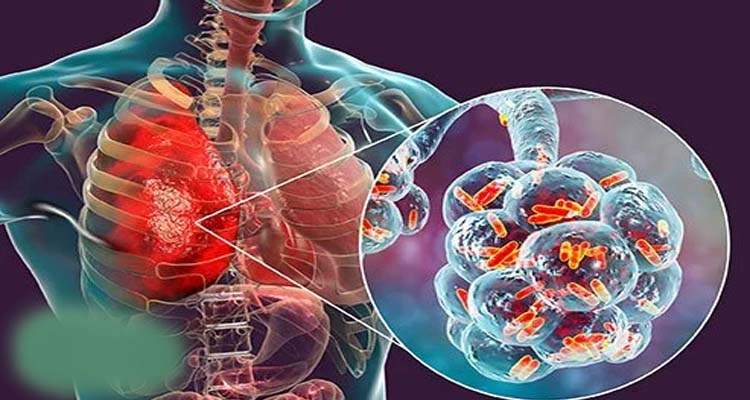
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can cause mild to severe illness in people of all ages. Signs of pneumonia can include coughing, fever, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, rapid breathing or shortness of breath, chills, or chest pain. Certain people are more likely to become ill with pneumonia. This includes adults 65 years of age or older and children younger than 5 years of age. People up through 64 years of age who have underlying medical conditions (like diabetes or HIV/AIDS) and people 19 through 64 who smoke cigarettes or have asthma are also at increased risk for getting pneumonia.
Encourage friends and loved ones with certain health conditions, like diabetes and asthma, to get vaccinated against the flu and bacterial pneumonia.
When bacteria, viruses or, rarely, fungi living in your nose, mouth, sinuses, or the environment spread to your lungs, you can develop pneumonia or other infections. You can catch the bacteria or viruses from people who are infected with them, whether they are sick or not.
Pneumonia developed during or following a stay in a healthcare facility (like hospitals, long-term care facilities, and dialysis centers) is called healthcare-associated pneumonia (HCAP), which includes hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP).